AOF(append only file)持久化:以独立日志的方式记录每次写命令,重启时再重新执行AOF文件中的命令达到恢复数据的目的。AOF的主要作用是解决了数据持久化的实时性,目前已经是Redis持久化的主流方式。
开启AOF功能需要设置配置:appendonly yes,AOF文件名通过appendfilename配置设置,默认文件名是appendonly.aof。保存路径同RDB持久化方式一致,通过dir配置指定。
appendonly默认是no,需要改成yes
# By default Redis asynchronously dumps the dataset on disk. This mode is
# good enough in many applications, but an issue with the Redis process or
# a power outage may result into a few minutes of writes lost (depending on
# the configured save points).
#
# The Append Only File is an alternative persistence mode that provides
# much better durability. For instance using the default data fsync policy
# (see later in the config file) Redis can lose just one second of writes in a
# dramatic event like a server power outage, or a single write if something
# wrong with the Redis process itself happens, but the operating system is
# still running correctly.
#
# AOF and RDB persistence can be enabled at the same time without problems.
# If the AOF is enabled on startup Redis will load the AOF, that is the file
# with the better durability guarantees.
#
# Please check http://redis.io/topics/persistence for more information.
appendonly no
文件名,默认是appendonly.aof
# The name of the append only file (default: "appendonly.aof")
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
AOF的工作流程操作:命令写入(append)、文件同步(sync)、文件重写(rewrite)、重启加载(load),如下图

- 所有的写入命令会追加到aof_buf(缓冲区)中
- AOF缓冲区根据对应的策略向硬盘做同步操作
- 随着AOF文件越来越大,需要定期对AOF文件进行重写,达到压缩的目的
- 当Redis服务器重启时,可以加载AOF文件进行数据恢复。
命令写入
AOF命令写入的内容直接是文本协议格式,即是RESP,Redis序列化协议
例如set hello world这条命令,在AOF缓冲区会追加如下文本
*3\r\n$3\r\nset\r\n$5\r\nhello\r\n$5\r\nworld\r\n
AOF会把命令追加到aof_buf中的好处:Redis使用单线程响应命令,如果每次写AOF文件命令都直接追加到硬盘,那么性能完全取决于当前硬盘负载。先写入缓冲区aof_buf中,还有另一个好处,Redis可以提供多种缓冲区同步硬盘的策略,在性能和安全性方面做出平衡
文件同步
Redis提供了多种AOF缓冲区同步文件策略,由参数appendfsync控制
# The fsync() call tells the Operating System to actually write data on disk
# instead of waiting for more data in the output buffer. Some OS will really flush
# data on disk, some other OS will just try to do it ASAP.
#
# Redis supports three different modes:
#
# no: don't fsync, just let the OS flush the data when it wants. Faster.
# always: fsync after every write to the append only log. Slow, Safest.
# everysec: fsync only one time every second. Compromise.
#
# The default is "everysec", as that's usually the right compromise between
# speed and data safety. It's up to you to understand if you can relax this to
# "no" that will let the operating system flush the output buffer when
# it wants, for better performances (but if you can live with the idea of
# some data loss consider the default persistence mode that's snapshotting),
# or on the contrary, use "always" that's very slow but a bit safer than
# everysec.
#
# More details please check the following article:
# http://antirez.com/post/redis-persistence-demystified.html
#
# If unsure, use "everysec".
# appendfsync always
appendfsync everysec
# appendfsync no
系统调用write和fsync说明
– write操作会触发延迟写(delayed write)机制。Linux在内核提供页缓冲区用来提高硬盘IO性能。write操作在写入系统缓冲区后直接返回。同步硬盘操作依赖于系统调度机制,例如:缓冲区页空间写满或达到特定时间周期。同步文件之前,如果此时系统故障宕机,缓冲区内数据将丢失
– fsync针对单个文件操作(比如AOF文件),做强制硬盘同步,fsync将阻塞直到写入硬盘完成后返回,保证了数据持久化
– 配置为always时,每次写入都要同步AOF文件,在一般的SATA硬盘上,Redis只能支持大约几百TPS写入,显然跟Redis高性能特性背道而驰,不建议配置
– 配置为no,由于操作系统每次同步AOF文件的周期不可控,而且会加大每次同步硬盘的数据量,虽然提升了性能,但数据安全性无法保证
– 配置为everysec,是建议的同步策略,也是默认配置,做到兼顾性能和数据安全性。理论上只有在系统突然宕机的情况下丢失1秒的数据
重写机制
随着命令不断写入AOF,文件会越来越大,为了解决这个问题,Redis引入AOF重写机制压缩文件体积。AOF文件重写是把Redis进程内的数据转化为写命令同步到新AOF文件的过程
- 重写后的AOF文件会变小的原因:
- 进程内已经超时的数据不再写入文件
- 旧的AOF文件含有无效命令,如del key1、hdel key2、srem keys、set a 111、set a 222等。重写使用进程内数据直接生成,这样新的AOF文件只保留最终数据的写入命令
- 多条写命令可以合并为一个,如:lpush list a、lpush list b、lpush list c可以转化为:lpush list a b c。为了防止单条命令过大造成客户端缓冲区溢出,对于list、set、hash、zset等类型操作,以64个元素为界拆分为多条
AOF重写降低了文件占用空间,除此之外,另一个目的是:更小的AOF文件可以更快地被Redis加载
AOF重写过程可以手动触发和自动触发
手动触发:直接调用bgrewriteaof命令
自动触发:根据auto-aof-rewrite-min-size和auto-aof-rewrite-percentage参数确定自动触发时机
# Automatic rewrite of the append only file.
# Redis is able to automatically rewrite the log file implicitly calling
# BGREWRITEAOF when the AOF log size grows by the specified percentage.
#
# This is how it works: Redis remembers the size of the AOF file after the
# latest rewrite (if no rewrite has happened since the restart, the size of
# the AOF at startup is used).
#
# This base size is compared to the current size. If the current size is
# bigger than the specified percentage, the rewrite is triggered. Also
# you need to specify a minimal size for the AOF file to be rewritten, this
# is useful to avoid rewriting the AOF file even if the percentage increase
# is reached but it is still pretty small.
#
# Specify a percentage of zero in order to disable the automatic AOF
# rewrite feature.
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb
auto-aof-rewrite-min-size:表示运行AOF重写时文件最小体积,默认为64MB
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage:代表当前AOF文件空间(aof_current_size)和上一次重写后AOF文件空间(aof_base_size)的比值
自动触发时机=aof_current_size>auto-aof-rewrite-min-size&&(aof_current_size-aof_base_size)/aof_base_size>=auto-aof-rewrite-percentage
其中aof_current_size和aof_base_size可以在info Persistence统计信息中查看
AOF重写运作流程如下图

1.执行AOF重写请求
2.父进程执行fork创建子进程,开销等同于bgsave过程
3.1 主进程fork操作完成后,继续响应其他命令。所有修改命令依然写入AOF缓冲区并根据appendfsync策略同步到硬盘,保证原有AOF机制正确性
3.2 由于fork操作运用写时复制技术,子进程只能共享fork操作时的内存数据。由于父进程依然响应命令,Redis使用“AOF重写缓冲区”保存这部分新数据,防止新AOF文件生成期间丢失这部分数据
4 子进程根据内存快照,按照命令合并规则写入到新的AOF文件。每次批量写入硬盘数据量由配置aof-rewrite-incremental-fsync控制,默认为32MB,防止单次刷盘数据过多造成硬盘阻塞
5.1 新AOF文件写入完成后,子进程发送信号给父进程,父进程更新统计信息,具体见info persistence下的aof_*相关统计
5.2 父进程把AOF重写缓冲区的数据写入到新的AOF文件
5.3 使用新AOF文件替换老文件,完成AOF重写
重启加载
AOF和RDB文件都可以用于服务器重启时的数据恢复,下图表示Redis持久化文件加载流程
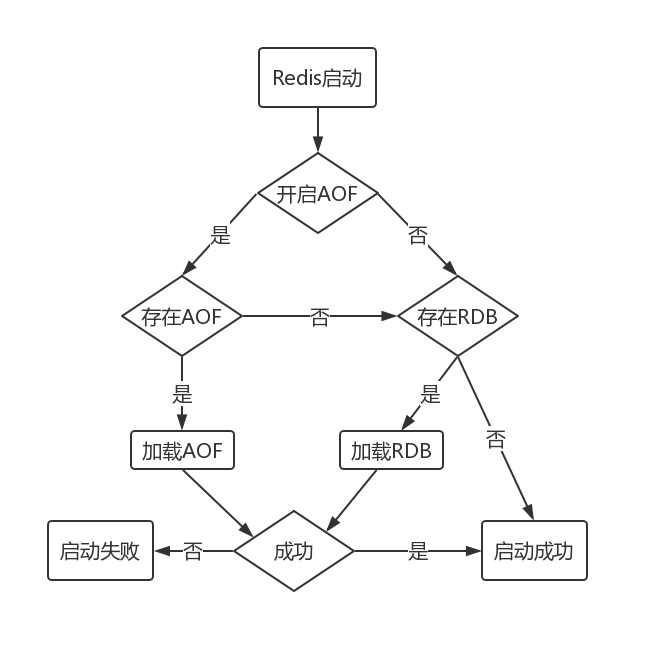
文件校验
加载损坏的AOF文件时会拒绝启动,并打印如下日志:
# Bad file format reading the append only file: make a backup of your AOF file,then use ./redis-check-aof --fix
对于错误格式的AOF文件,先进行备份,然后采用redis-check-aof–fix命令进行修复,修复后使用diff-u对比数据的差异,找出丢失的数据,有些可以人工修改补全。
AOF文件可能存在结尾不完整的情况,比如机器突然掉电导致AOF尾部文件命令写入不全。Redis为我们提供了aof-load-truncated配置来兼容这种情况,默认开启。加载AOF时,当遇到此问题时会忽略并继续启动,同时打印如下警告日志:
# !!! Warning: short read while loading the AOF file !!!
# !!! Truncating the AOF at offset 397856725 !!!
# AOF loaded anyway because aof-load-truncated is enabled
此为配置文件中aof-load-truncated的默认配置和官方的详细说明文档
# An AOF file may be found to be truncated at the end during the Redis
# startup process, when the AOF data gets loaded back into memory.
# This may happen when the system where Redis is running
# crashes, especially when an ext4 filesystem is mounted without the
# data=ordered option (however this can't happen when Redis itself
# crashes or aborts but the operating system still works correctly).
#
# Redis can either exit with an error when this happens, or load as much
# data as possible (the default now) and start if the AOF file is found
# to be truncated at the end. The following option controls this behavior.
#
# If aof-load-truncated is set to yes, a truncated AOF file is loaded and
# the Redis server starts emitting a log to inform the user of the event.
# Otherwise if the option is set to no, the server aborts with an error
# and refuses to start. When the option is set to no, the user requires
# to fix the AOF file using the "redis-check-aof" utility before to restart
# the server.
#
# Note that if the AOF file will be found to be corrupted in the middle
# the server will still exit with an error. This option only applies when
# Redis will try to read more data from the AOF file but not enough bytes
# will be found.
aof-load-truncated yes
AOF追加阻塞
当开启AOF持久化时,常用的同步硬盘的策略是everysec,用于平衡性能和数据安全性。对于这种方式,Redis使用另一条线程每秒执行fsync同步硬盘。当系统硬盘资源繁忙时,会造成Redis主线程阻塞。如下图所示:
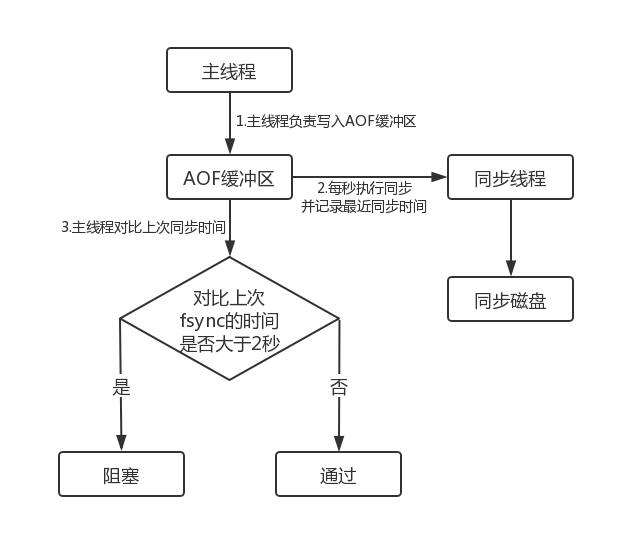
- 主线程负责写入AOF缓冲区
-
AOF线程负责每秒执行一次同步磁盘操作,并记录最近一次同步时间
-
主线程负责对比上次AOF同步时间:
- 如果距上次同步成功时间在2秒内,主线程直接返回
- 如果距上次同步成功时间超过2秒,主线程将会阻塞,直到同步操作完成
AOF阻塞问题定位:
- 发生AOF阻塞时,Redis输出如下日志,用于记录AOF fsync阻塞导致拖慢Redis服务的行为:
Asynchronous AOF fsync is taking too long (disk is busy). Writing the AOF buffer
without waiting for fsync to complete, this may slow down Redis
-
每当发生AOF追加阻塞事件发生时,在info Persistence统计中,aof_delayed_fsync指标会累加,查看这个指标方便定位AOF阻塞问题
-
AOF同步最多允许2秒的延迟,当延迟发生时说明硬盘存在高负载问题,可以通过监控工具如iotop,定位消耗硬盘IO资源的进程